How to apply Knowledge Management – KM in validation

Knowledge Management is the process of capturing, distributing, managing, and effectively using knowledge and information within an organization. These assets can be documents, policies, procedures, experiences, among several other contents that aim to acquire, organize, and transfer knowledge.
Usually, companies have knowledge of portals, or databases, that allow them to share business information, such as intranets and wikis.
The idea, therefore, is to use an experience of similar projects and lessons learned, for more assertive and faster decision-making in other projects.

The first reference of KM in the field of pharmaceutical quality was ICH Q8 in 2005 as a tool used with QRM (Quality Risk Management) for a more systematic approach of Quality by Design (QbD) from development throughout the product life cycle.
Three years later, ICH Q10 identified KM and QRM as the enablers of an effective Pharmaceutical Quality System, providing the means for scientific and risk-based decision-making regarding product quality.
ICH 10: Knowledge management
For example, development activities using scientific approaches provide knowledge for product and process understanding.
Knowledge management is a systematic approach to acquire, analyze, store, and disseminate information related to products, manufacturing processes, and components.
Sources of knowledge include, but are not limited to, prior knowledge (public domain or documented internally); pharmaceutical development studies; transfer activities of technology; studies of process validation throughout the product life cycle; manufacturing experience; innovation; continuous improvement; and activities of change management.

Since its publication, the pharmaceutical industry has made progress, especially in adopting QRM into systems and processes. However, the industry has been slow in implementing KM, thus missing out on the advantages of its use.
Due to the relevance of the topic, ISPE® has published a guide for pharmaceutical industries (ISPE® Good Practice Guide: Knowledge Management in the Pharmaceutical Industry) that promotes the union of KM with QRM for better business performance by increasing efficiency, building more robust processes, facilitating continuous improvement, and creating an engaged knowledge workforce.
What is the benefit of applying KM:
- Better, more assertive and faster risk-based decision-making;
- Maintenance and increase of the quality of product and service delivery even in case of employee turnover1
- Access to information;
- Increase of team collaboration;
- Improvement of communication;
- Optimization of employee training.
It can be a business strategy, especially during a wave of voluntary resignations, as a way to retain knowledge.
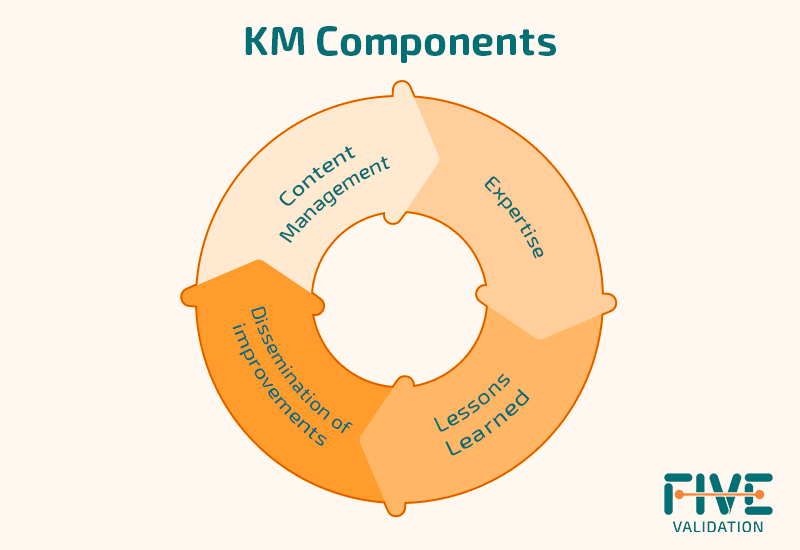
Basically, we can divide KM into 4 components:
Software for Applying KM in Validation
The most immediate and obvious component within KM is content management. However, for its effective application, the use of technology and specificity is fundamental.
The ISPE® guide itself, which was cited in this article, promotes the use of technology, since the amount of data, information and knowledge available is enormous within an organization and managing this volume of data, variety and complexity can be challenging.
Therefore knowledge, maturity assessment and expertise mapping can be the key to identify gaps, opportunities and improvements in the areas in question.
GO!FIVE®, a cloud-based validation/qualification software, is the only solution on the market with content in the database, built on the experience of over 1000 projects and updated continually.
Despite validation not being a new requirement, there is still a lack of knowledge, and material that supports professionals to achieve compliance and optimization of GxP processes (impact on good practices).
Although each company has its own idiosyncrasies, there are several standard validation/qualification processes, requirements, risks and tests that are common for many companies. The library contains only suggestions, where an expert is free to either use or adapt it at their discretion. All traceability is automatically maintained by the system.

Updating libraries, as well as creating new ones, is done regularly by FIVE Validation team via libraries that are public.
Therefore, with planning, content is always available, and it is not necessary for a client’s expert to start projects from scratch.
It is also possible for a client to manage their own content via creating private libraries (i.e., creating and/or translating pre-prepared validations in their own database) as well as saving them for similar validation/qualification projects in their tenant section.
With all things considered, the value is self-evident for our clients.
If you want to know more about all the resources/tools available in the system, CLICK HERE and schedule a meeting with our team.
Also, if you would like to receive more information, you may contact us via e-mail at [email protected].
Author: Lílian Ribeiro
- Sales Coordinator at FIVE Validation;
- Technical and commercial experience of almost four years in food industry in the quality/quality control area and four years in the healthcare/pharmaceutical sectors.
- Enthusiast of paperless validation for life science companies;
- Experience in validation and qualification projects: VLMS, ERPs, EQMS, Automation (PW) and IT Infrastructure Qualification.
References:
- ICH Q8
- ICH Q10
- https://ispe.org/publications/guidance-documents/good-practice-guide-knowledge-management-pharmaceutical-industry
- https://www.kmworld.com/About/What_is_Knowledge_Management



