What is IT Infrastructure Qualification?
Information Technology Infrastructure Qualification (IT IQ) is a process commonly found in regulated industries, particularly in Life Sciences sectors such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and medical devices.
Its primary purpose is to guarantee the dependability, security, and adherence to compliance standards of information technology systems and infrastructure deployed in product development, manufacturing, testing, and distribution. This process entails a series of activities and documentation aimed at substantiating that the IT infrastructure aligns with defined regulatory prerequisites and quality benchmarks. The following outlines the key facets of IT infrastructure qualification:
Are you uncertain about the intricacies of infrastructure qualification? Rest assured, the FIVE Validation team brings decades of experience to the table.
Introducing GO!FIVE® software is a cutting-edge platform equipped with libraries and templates designed to streamline validation and qualification procedures.
Whether it's IT or OT infrastructure qualification, we've got you covered!
What is OT Infrastructure Qualification?
OT infrastructure qualification, also known as Operational Technology Infrastructure Qualification for the Life Science industry, is a process like IT infrastructure qualification but focuses on the systems and components used in the operational technology (OT) environment.
The OT environment typically includes industrial control systems (ICS), supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and other hardware and software components that control and monitor industrial processes in various industries, such as manufacturing, energy, and utilities.
Here are key aspects and considerations of OT infrastructure qualification:
Explore our services page now and discover how FIVE Validation can enhance your work!
IT and OT infrastructure as a Commodity
IT (Information Technology) and OT (Operational Technology) infrastructures are often referred to as commodities because they have become standardized and widely available resources that are essential for the operation of modern businesses and industrial processes.
Here are a few reasons why IT and OT infrastructure can be considered commodities for the Life Science industry:
Here are key aspects and considerations of OT infrastructure qualification:
Scope of Infrastructure Qualification
The figure below illustrates the extent of infrastructure considerations and highlights the necessity of including certain IT-related business processes within the purview of qualified infrastructure.
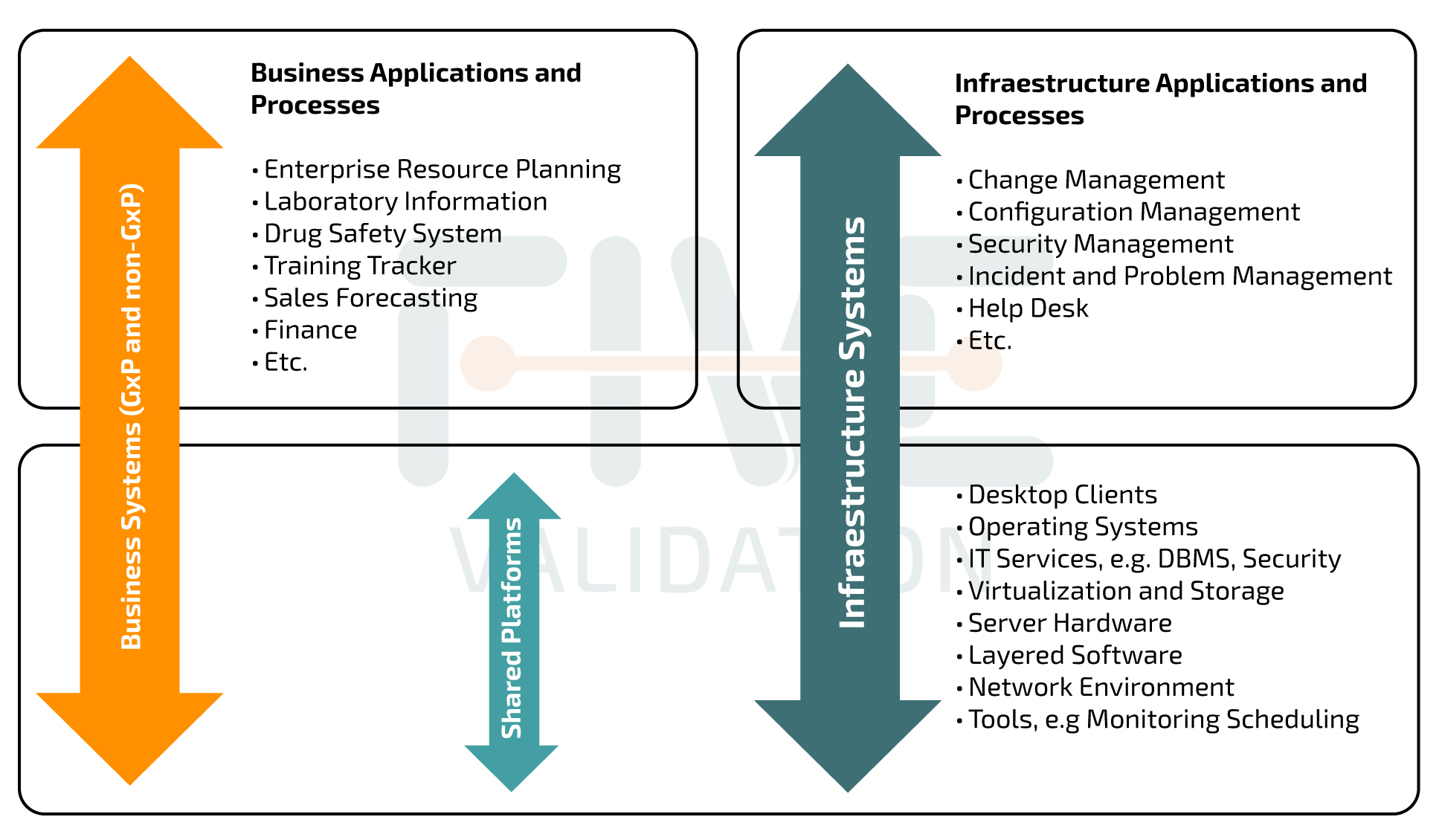
Inspired on figure 19.1 page 164, appendix M1 from GAMP5® second edition. Relationship of IT infrastructure and processes with business systems and processes.
Infrastructure Qualification versus Application Validation
A regulated company adopts a structured approach when implementing an application to fulfill its business requirements. This involves defining requirements, configuring the application as needed, conducting risk-based verification, establishing operational controls, and maintaining it in a controlled state – collectively known as validation.
IT Processes in Scope for Infrastructure Qualification
Many IT-managed processes play a crucial role in maintaining the controlled state of applications. Various resources, such as ITIL, offer excellent frameworks for managing these IT business processes. Some of these processes necessitate input from business application users. For instance, business input is essential for defining expected service levels, including help desk hours, response times, and other related factors.


